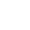The Klow Blend combines four research peptides, BPC-157, TB-500, KPV, and GHK-Cu, formulated for studies on cellular repair, immune modulation, and extracellular matrix regulation. BPC-157 is a 15 amino acid gastric peptide fragment that modulates nitric oxide and growth factor pathways. TB-500, a segment of Thymosin Beta-4, regulates actin polymerization and tissue remodeling. KPV, derived from the C-terminal region of alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone, modulates NF-κB and cytokine signaling. GHK-Cu, a copper(II)-complexed tripeptide, influences metalloprotein activity and redox balance. Together, these peptides are used in research examining regeneration, inflammation, and peptide–metal interaction mechanisms.
Overview
The BPC-157+ TB-500(Thymosin Beta-4) + KPV+ GHK-Cu Blend is a multi-peptideresearch formulation designed to support investigation into synergistic mechanisms of tissue repair, inflammation regulation, and regenerative biology. Each peptide included in this blend has independently demonstrated robust activity in preclinical models of woundhealing, immune modulation, angiogenesis, and protection against tissue degeneration.
While BPC-157, TB-500, GHK-Cu, and KPV share overlapping biological themes-namely cytoprotection, inflammation control, and regenerative signaling–they act through distinct molecular pathways. Combining these peptides into a single formulation enables researchers to study how complementary mechanisms converge to influence healing kinetics, tissue quality, and long-term functional outcomes.
This blend was developed to simplify experimental design by reducing the logisticalcomplexity associated with administering multiple peptides independently. By consolidating these peptides into one formulation, researchers may focus on mechanistic interrogation, biomarker analysis, and outcome measurement rather than protocol complexity.
Biochemical Characteristics
BPC-157 is a synthetic pentadecapeptide derived from a naturally occurring gastric cytoprotective protein known as Body Protective Compound (BPC). It is notable for its stability in gastric environments, rapid systemic distribution, and profound influence on nitric oxide signaling and gene expression related to vascular and immune function.
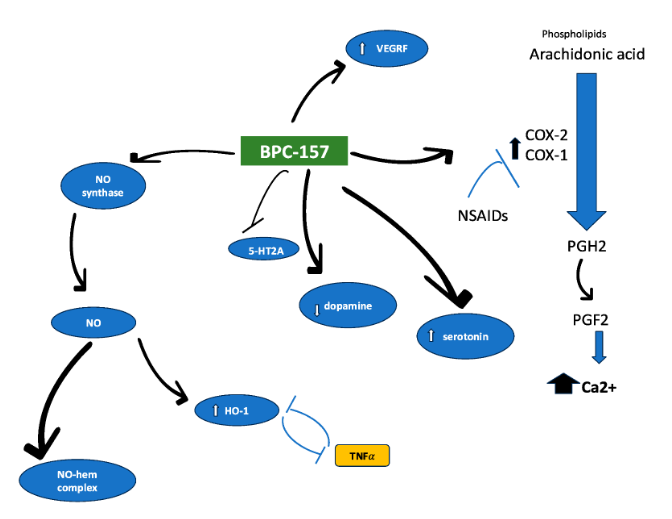
TB-500 is a synthetic peptide based on thymosin beta-4, an actin-binding protein involved in cytoskeletal dynamics, cell migration, and angiogenesis. TB-500 retains both the actin- sequestering properties of thymosin beta-4 and its “moonlighting” function as a regulator
of gene expression and inflammatory signaling.
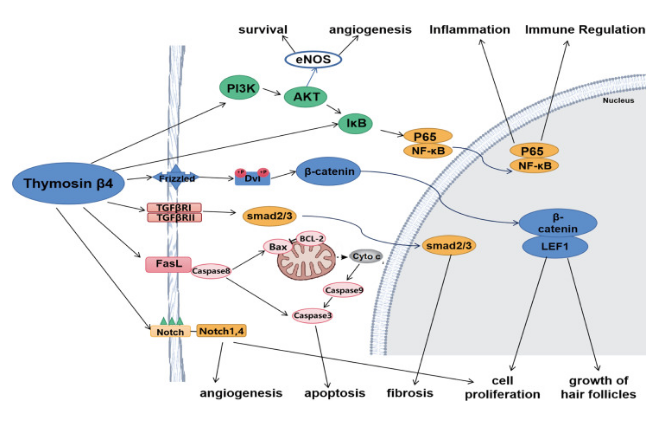
GHK-Cu is a copper-complexed tripeptide (Gly-His-Lys-Cu²+) naturally present in human plasma, saliva, and urine. It plays a regulatory role in extracellular matrix remodeling,antioxidant defense, and gene expression related to tissue repair and immune balance.
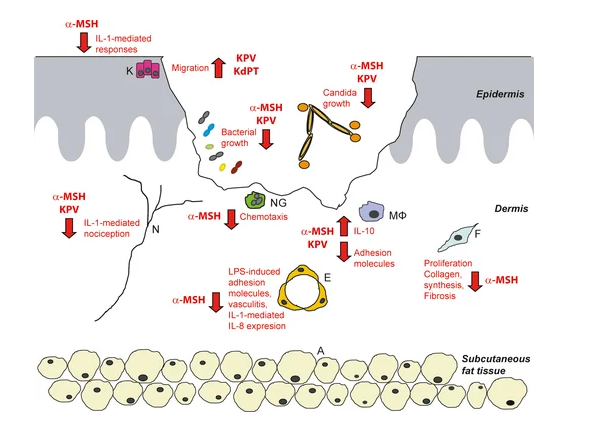
KPV is a tripeptide derived from the C-terminal sequence of a-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (a-MSH). Despite its small size, KPV exhibits potent anti-inflammatory activity and demonstrates selective action in inflamed tissues while largely sparing normal immune responses.
Research Applications
This peptide blend is of interest for research in tissue regeneration, musculoskeletal injury, inflammatory disorders, fibrosis prevention, and aging-associated tissue decline. Investigational models include skin wounds, tendon and ligament injury, muscle degeneration, gastrointestinal inflammation, pulmonary injury, and neuroinflammatory conditions.
The combination allows exploration of how coordinated modulation of nitric oxide signaling, cytokine production, extracellular matrix remodeling, and stem-cell-related pathways influences healing speed, scar quality, and long-term tissue function. Additional areas of research interest include angiogenesis, immune cell recruitment, oxidative stress mitigation, and regulation of gene expression patterns associated with chronic inflammation and aging.
Pathway / Mechanistic Context
BPC-157 exerts a central role in this blend through its modulation of nitric oxide (NO) signaling. It influences endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) activity via Src-Caveolin-1 interactions, promoting vascular stability, angiogenesis, and immune regulation. These effects are closely tied to its ability to alter expression of genes such as Egr, Nos, Vegf,and Srf.
TB-500 complements this activity by regulating cytoskeletal dynamics through actin sequestration while simultaneously modulating inflammatory signaling pathways such as NF-kB,Tollike receptor cascades,PI3K/Akt/eNOS, and TGF-β. These combined actions support cell migration, reduce fibrosis, and enhance tissue regeneration.
GHK-Cu contributes by balancing extracellular matrix turnover through coordinated activation of metalloproteinases and anti-proteases. It also suppresses pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-a, IL-6), scavenges reactive oxygen species, and influences gene networks involved in antioxidant defense and tissue remodeling.
KPV provides high-level regulation of inflammation by inhibiting NF-kB signaling, reducing adhesion molecule expression, and suppressing downstream cytokines such as IL-8.Notably, KPV exhibits tissue-selective activity, acting primarily where inflammation is excessive while preserving physiological immune responses necessary for healing.
Preclinical studies of BPC-157 demonstrate accelerated wound closure, enhanced angiogenesis, reduced inflammatory infiltration, and improved functional outcomes in tendon,muscle,gastrointestinal,and cardiovascular injury models.
TB-500 has shown efficacy in promoting cell migration, reducing fibrosis, and enhancing regeneration in cardiac,muscular, ocular, and dermal injury models.
GHK-Cu has been shown to improve wound healing rates, reduce infection incidence, modulate gene expression associated with tissue regeneration, and protect against oxidative and inflammatory injury in pulmonary,dermal, and neural tissues.
KPV has demonstrated broad anti-inflammatory activity across multiple organ systems, with particular efficacy in reducing scarring and pathological inflammation.
Collectively, these peptides demonstrate complementary effects that suggest additive or synergistic outcomes when combined, particularly in models of chronic inflammation, delayed healing, and age-associated tissue degeneration.
Post time: Jan-19-2026