What Is Cagrilintide?
Cagrilintide is a long-acting peptide engineered to mimic the function of amylin, a hormone normally released alongside insulin by pancreatic beta cells. Endogenous amylin supports appetite regulation and delays gastric emptying, contributing to glucose and energy balance.
However, its clinical utility is limited due to rapid enzymatic breakdown. This amylin analog peptide addresses this issue through molecular modifications that enhance stability and extend its half-life, allowing for convenient once-weekly subcutaneous administration in clinical protocols.
How Cagrilintide Works in the Body
Unlike incretin-based therapies, cagrilintide acts primarily on amylin and calcitonin receptors in the brain. This interaction enhances satiety signaling, reducing hunger and promoting earlier meal termination. The prolonged gastric emptying further supports sustained postprandial fullness, a mechanism especially helpful for patients who struggle with frequent snacking or binge eating patterns.
Cagrilintide also shows an ability to reduce overall caloric intake and food cravings, particularly for high-fat or high-sugar foods. When paired with semaglutide, which targets GLP-1 receptors, the result is a complementary pathway approach, tapping into both incretin and amylin networks for broader metabolic control. This makes combination therapy particularly attractive in resistant cases or where long-term results are needed.
Cagrilintide vs. Semaglutide: Key Differences and Synergies
The comparison of Cagrilintide vs semaglutide highlights how dual-pathway modulation may offer more robust results than single-agent approaches alone.
While semaglutide remains the cornerstone of GLP-1-based weight management, cagrilintide introduces a new dimension by activating amylin receptors. Their mechanisms differ, but their goals overlap: appetite suppression, reduced energy intake, and improved glycemic regulation.
Clinical trials show enhanced outcomes when cagrilintide and semaglutide are combined. Patients not only experience more weight loss but also improved satiety and fewer cravings. Practitioners should monitor overlapping side effects like nausea and titrate doses accordingly.
What Clinical Trials Tell Us
Cagrilintide clinical trials have shown promising outcomes in reducing appetite, improving adherence, and driving sustainable weight reduction.
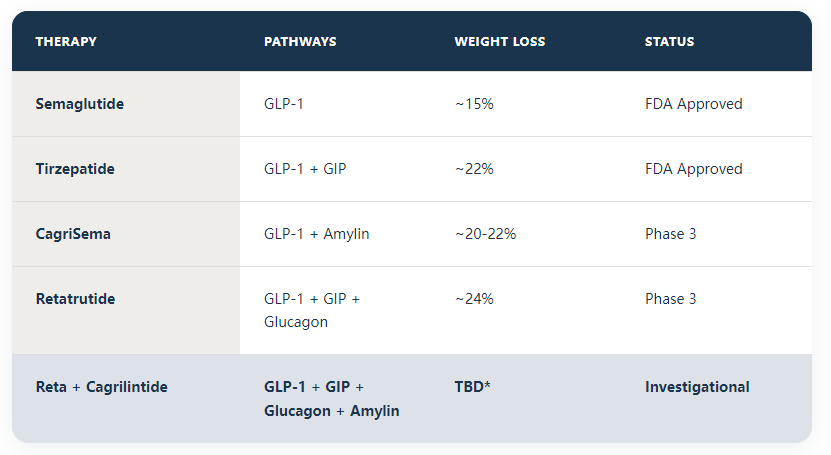
Several clinical trials, including data published in The New England Journal of Medicine, have demonstrated that cagrilintide significantly reduces body weight in patients with obesity. When compared to placebo, patients receiving cagrilintide alone lost an average of 5-10% of their body weight. These effects were magnified in combination therapy protocols, with some studies noting weight reductions of up to 15% when paired with semaglutide.
Secondary endpoints in trials include reductions in waist circumference, visceral fat mass, appetite scores, and daily caloric intake. While cagrilintide is not yet FDA-approved, its ongoing development suggests strong potential as part of a new pharmacologic framework in obesity care.
Why Cagrilintide Could Change Obesity Care?
The mechanism behind Cagrilintide weight loss lies in its ability to enhance satiety and reduce meal frequency without the use of stimulants. Cagrilintide’s once-weekly dosing enhances patient adherence, especially when compared to daily or more frequent injectables.
Furthermore, cagrilintide peptide therapy offers an alternative for patients who plateau on GLP-1 monotherapy or cannot tolerate its full dosage. Its stimulant-free mechanism reduces the risk of anxiety or cardiovascular stress, making it suitable for a broader range of patient profiles, including those with type 2 diabetes or metabolic syndrome.
FAQs
Is Cagrilintide better than tirzepatide?
These two peptides work via different pathways. While tirzepatide is a dual GLP-1/GIP agonist, cagrilintide acts via the amylin system. Ongoing trials are comparing outcomes.
How much weight can you lose on Cagrilintide?
In clinical trials, participants lost between 5% and 15% of body weight, especially when combined with semaglutide. Results vary by patient profile and dosage.
Does Cagrilintide slow gastric emptying?
Yes, one of its primary mechanisms is delayed gastric emptying, which enhances feelings of fullness and reduces meal frequency.
How long does Cagrilintide stay in your system?
Cagrilintide has a long half-life, supporting once-weekly subcutaneous dosing. This increases patient convenience and treatment adherence.
Can Cagrilintide be taken alone?
Yes, it is being studied both as monotherapy and in combination with GLP-1 drugs. However, greater weight loss has been observed when used together with semaglutide.
Post time: Jan-26-2026